

The discrepancy is due primarily to neglecting the (then unknown) effect of rapidly-fluctuating temperature in a sound wave (in modern terms, sound wave compression and expansion of air is an adiabatic process, not an isothermal process). Sir Isaac Newton's 1687 Principia includes a computation of the speed of sound in air as 979 feet per second (298 m/s). Objects moving at speeds greater than the speed of sound ( Mach 1) are said to be traveling at supersonic speeds. The ratio of the speed of an object to the speed of sound (in the same medium) is called the object's Mach number. In fluid dynamics, the speed of sound in a fluid medium (gas or liquid) is used as a relative measure for the speed of an object moving through the medium. The speed of shear waves is determined only by the solid material's shear modulus and density. The speed of compression waves in solids is determined by the medium's compressibility, shear modulus, and density. Shear waves in solids usually travel at different speeds than compression waves, as exhibited in seismology. Sound waves in solids are composed of compression waves (just as in gases and liquids) and a different type of sound wave called a shear wave, which occurs only in solids.
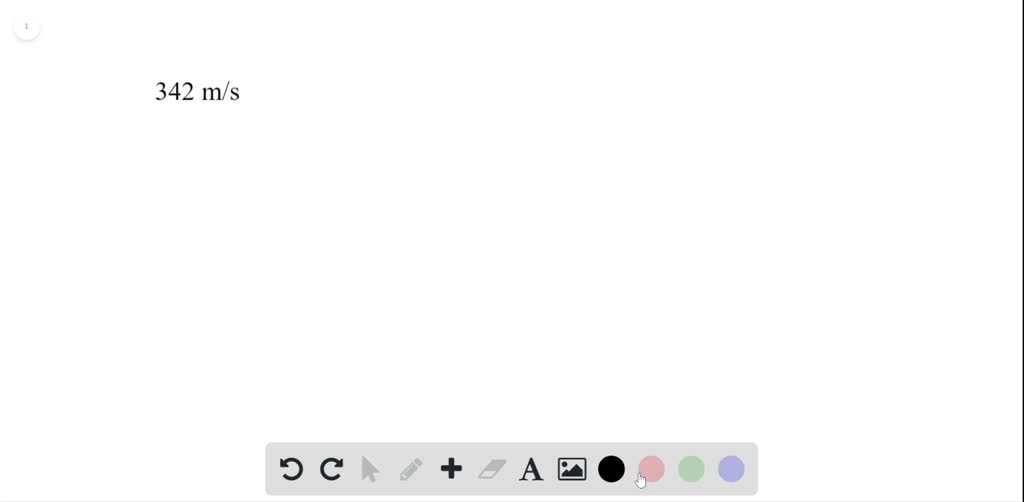
In theory, the speed of sound is actually the speed of vibrations. In an exceptionally stiff material such as diamond, sound travels at 12,000 metres per second (39,000 ft/s), - about 35 times its speed in air and about the fastest it can travel under normal conditions. For example, while sound travels at 343 m/s in air, it travels at 1,481 m/s in water (almost 4.3 times as fast) and at 5,120 m/s in iron (almost 15 times as fast). However, the speed of sound varies from substance to substance: typically, sound travels most slowly in gases, faster in liquids, and fastest in solids. In colloquial speech, speed of sound refers to the speed of sound waves in air. The speed has a weak dependence on frequency and pressure in ordinary air, deviating slightly from ideal behavior. The speed of sound in an ideal gas depends only on its temperature and composition. More simply, the speed of sound is how fast vibrations travel. It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At 20 ☌ (68 ☏), the speed of sound in air is about 343 metres per second (1,125 ft/s 1,235 km/h 767 mph 667 kn), or one kilometre in 2.91 s or one mile in 4.69 s. Table showing various speed of sound measurements converted to feet per second.The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. Speed of Sound to Foot per Second Conversion Table The velocity in feet per second is equal to the distance in feet divided by time in seconds. For example, ft/s is expressing a change in length or distance relative to a change in time.įeet per second can be expressed using the formula: In the expressions of units, the slash, or solidus (/), is used to express a change in one or more units relative to a change in one or more other units. For example, 1 foot per second can be written as 1 ft/s, 1 ft/sec, or 1 fps. Feet per second can be abbreviated as ft/s, and are also sometimes abbreviated as ft/sec or fps. The foot per second is a US customary and imperial unit of speed. Feet per second are a measurement of speed expressing the distance traveled in feet in one second.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
